
When it comes to certification you can’t afford for anything to fail, especially the MVHR that’s fundamental for a passive house or anything close. And of all the MVHR requirements, running below 25 Decibels on boost is the most difficult to achieve. That’s almost half as quiet as a regular Part-F compliant MVHR that must run below 30 Decibels.
Technically speaking, 25dB(A) is 83% quieter than 30dB(A) because sound level doubles every 6dB(A) and intensity doubles every 3dB(A) .
It takes a lot more than a ‘Passivhaus certified’ badge on the machine to qualify for certification, that’s just the starting point. Not only must the MVHR designer create a system that fits, they must accurately predict the system pressure (air resistance) of the whole system from the exterior terminals through to the air valves in the rooms. Based on this (evidenced) system pressure they must then calculate the energy consumption, or Specific Fan Power, along with acoustic performance of the proposed design.
All calculations better be accurate because Passivhaus guidelines ask for testing at the end of the project, and the ‘as-constructed’ test data should be added to the final PHPP model. There’s no such thing as an Energy Performance Gap with Passivhaus.
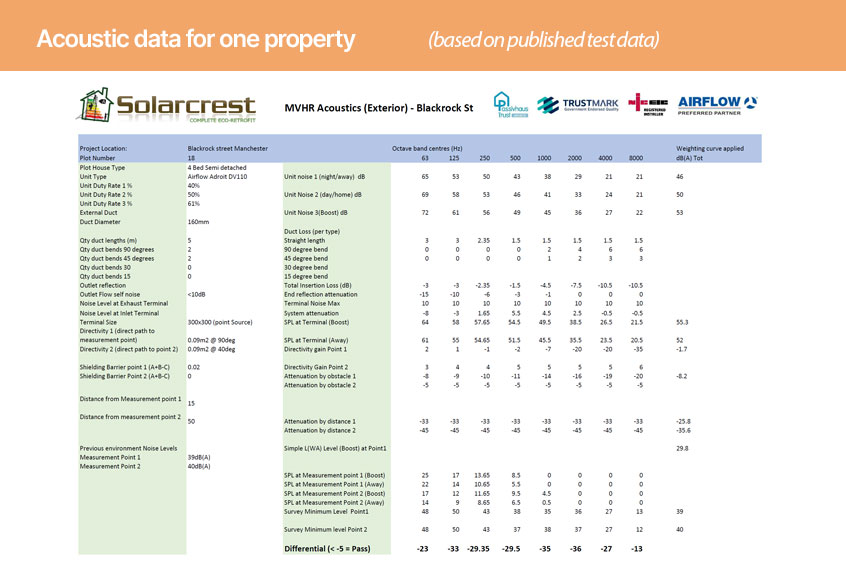
Every component used in the system must have published air pressure data from the manufacturer; the exterior grilles or roof terminals, the mass flow ducting, the machine, distribution manifolds and radial pipes, or the branch pipes and attenuators. Most exterior terminals are designed for extract-only ventilation, so only have data for air movement in one direction, from inside to outside the building. But MVHR has an air intake as well as an exhaust, so you need published data for air moving from outside to inside the building, which severely limits your options.
On the ducting itself, every single bend adds more pressure, so the last thing you need is an installer forced to add more bends because the ‘indicative’ design they’re following doesn’t fit. Even a small increase above the ‘as-designed’ air resistance can jeopardise performance if not final certification.
When you know the total air resistance on the system you can calculate the Specific Fan Power needed to deliver the required ventilation rates. The maximum figure, the power used to deliver boost ventilation, must comply with Approved Document F as well as Passivhaus. Finally, with accurate pressure and power data, supported by evidence, you can work out the worst-case acoustic performance. Passivhaus certifiers should ask for this performance data before you start.
Trusting the system goes in exactly as designed and then runs exactly as designed, i.e. very quietly and very efficiently, be prepared for the Passivhaus certifier to ask for evidence that the system works as planned. That means the MVHR commissioner must not only balance the system and set the flow rates, they’ll also need to measure the ‘in use’ energy consumption and potentially the acoustic performance using a calibrated sound meter.
Knowing this at the outset should help you find the right provider.
Here’s our advice